This document describes the procedure to enable TLS encryption for Expertflow CX stateful components mainly Redis, MongoDB, PostgreSQL and ActiveMQ.
WARNINIG
This procedures requires redeployment of existing solution to enable SSL/TLS support in mongodb, redis, postgresql and activeMQ. Please take backup before proceeding with the procedure below and then restore when completed. For further details please consult Mongo, PostgreSQL Backup/Restore Procedure for EF-CX on Kubernetes ( manual procedure )
Redis
Redis should be deployed with these values in the values.yaml file
tls:
## @param tls.enabled Enable TLS traffic
##
enabled: true
## @param tls.authClients Require clients to authenticate
##
authClients: true
## @param tls.autoGenerated Enable autogenerated certificates
##
autoGenerated: true
Deploy the Redis using the helm command mentioned in the deployment guide. Once the Redis is deployed successfully, migrate the TLS certificate to Expertflow namespace by executing
kubectl get secret redis-crt -n ef-external -o yaml | sed 's/namespace: ef-external/namespace: expertflow/' | kubectl create -f -
Manual Verification:-
export all cert files using the following commands:-
mkdir /tmp/redis_certs/
CERTFILES=($(kubectl get secret redis-crt -n ef-external -o go-template='{{range $k,$v := .data}}{{$k}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}'))
for f in ${CERTFILES[*]}; do kubectl get secret redis-crt -n ef-external -o go-template='{{range $k,$v := .data}}{{ if eq $k "'$f'"}}{{$v | base64decode}}{{end}}{{end}}' > /tmp/redis_certs/${f} 2>/dev/null; done
Export Redis Password:-
export REDIS_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace ef-external redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
Start a Redis client pod:-
kubectl run --namespace ef-external redis-client --env REDIS_PASSWORD=$REDIS_PASSWORD --image gitimages.expertflow.com/general/redis:CIM-4292-6.2-debian-10-k8s --command -- sleep infinity
Now you can mount the secret redis-crt inside the client pods and use TLS certificates.
kubectl cp --namespace ef-external /tmp/redis_certs/tls.crt redis-client:/tmp/tls.crt
kubectl cp --namespace ef-external /tmp/redis_certs/tls.key redis-client:/tmp/tls.key
kubectl cp --namespace ef-external /tmp/redis_certs/ca.crt redis-client:/tmp/ca.crt
Exec into client pod:-
kubectl exec --tty -i redis-client \
--namespace ef-external -- bash
verify the connection using the following command in client pod:-
I have no name!@redis-client:/$ REDISCLI_AUTH="$REDIS_PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-master --tls --cert /tmp/tls.crt --key /tmp/tls.key --cacert /tmp/ca.crt redis-master:6379>
redis-master:6379>
redis-master:6379> CONFIG GET databases
1) "databases"
2) "16"
MongoDB
Deploy the mongoDB helm chart with these values changed
tls:
## @param tls.enabled Enable MongoDB(®) TLS support between nodes in the cluster as well as between mongo clients and nodes
##
enabled: true
## @param tls.autoGenerated Generate a custom CA and self-signed certificates
##
autoGenerated: true
Then deploy the solution using standard helm command as mentioned in the CX deployment guide. Once the mongoDB chart is deployed successfully, copy the secret containing TLS certificates using
kubectl get secret mongo-mongodb-ca -n ef-external -o yaml | sed 's/namespace: ef-external/namespace: expertflow/' | kubectl create -f -
For all CX related components, DEV can use this mongo-mongodb-ca by mounting it as a volume
Manual Verification
-
export all the cert files in
ef-externalnamespace using
mkdir /tmp/mongodb_certs
CERTFILES=($(kubectl get secret mongo-mongodb-ca -n ef-external -o go-template='{{range $k,$v := .data}}{{$k}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}'))
for f in ${CERTFILES[*]}; do kubectl get secret mongo-mongodb-ca -n ef-external -o go-template='{{range $k,$v := .data}}{{ if eq $k "'$f'"}}{{$v | base64decode}}{{end}}{{end}}' > /tmp/mongodb_certs/${f} 2>/dev/null; done
The above script will export all the certs to local directory /tmp/mongodb_certs.
-
Run the following command to export MongoDB Password:-
kubectl get secret --namespace ef-external mongo-mongodb -o jsonpath="{.data.mongodb-root-password}" | base64 -d
-
Run the mongoDB client pod
kubectl run --namespace ef-external mongo-mongodb-client --env="MONGODB_ROOT_PASSWORD=$MONGODB_ROOT_PASSWORD" --image docker.io/bitnami/mongodb:6.0.2-debian-11-r1 --command -- sleep infinity
-
copy the certificate files inside the client pod
kubectl -n ef-external cp /tmp/mongodb_certs mongo-mongodb-client:/tmp/
-
Connect to the mongoDB pod using SSL/TLS certs
kubectl -n ef-external exec -it mongo-mongodb-client -- bash
-
once inside the mongodb-client pod, combine both cert and key file using
cat /tmp/mongodb_certs/mongodb-ca-cert /tmp/mongodb_certs/mongodb-ca-key > /tmp/mongodb_certs/combined.pem
-
verify the connection using tls
mongosh admin --host "mongo-mongodb" \
--authenticationDatabase admin \
-u root \
-p $MONGODB_ROOT_PASSWORD \
--tls \
--tlsAllowInvalidHostnames \
--tlsAllowInvalidCertificates \
--tlsCertificateKeyFile /tmp/mongodb_certs/client-pem \
--tlsCAFile /tmp/mongodb_certs/client-pem
Sometimes, the mongodb client pod doesn’t inherit the MONGODB_ROOT_PASSWORD environment variable, and user will have to enter the password manually.
PostgreSQL
There are no special instructions required for the Postgresql database to enable TLS on the client side. A standard connection string should be used to connect to the PostgreSQL server.
ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ uses full duplex certificates as shown in this diagram:
ActiveMQ TLS enablement is not fully functional yet.
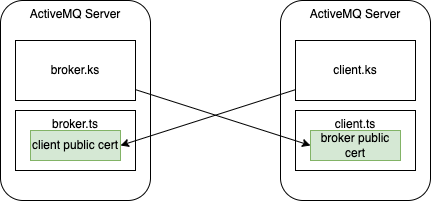
The client trust store contains a broker certificate to trust the broker, while the broker trust store stores the client certificate to trust the client. So it is a mutual trust when it comes to ActiveMQ TLS connection.
|
Client |
Port |
TLS Port |
|---|---|---|
|
Java (JMS) |
61616 |
61617 |
|
Node.js (STOMP) |
61613 |
61615 |
Java Client:
Use the following keystore and trust store in your ActiveMQ client, the relevant certificates are already added in the ActiveMQ Server.
Use port 61617 in this case. The example of URI is ssl://127.0.0.1:61617...
Stomp Client:
Use the following broker certificate to add to the client CA.
-
Broker Certificate: broker_cert
Use port 61615 in this case. The example of URI is stomp+nio+ssl://0.0.0.0:61615...