CX SIP Proxy streamlines call routing within Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) networks. CX SIP Proxy is a stateless routing control between SIP network elements. It acts as a load balancer, session controller and a security gateway for anything related to voice.
Experflow can control any calls via it’s SIP Proxy and start a conversation flow. In SIP, call flow can be relegated to a SIP B2BUA (such as Cisco CUBE or EF Media server), switch a call from one to the other (if self-service is required) or execute SIPREC forking for recording/ transcription/ voice biometrics. It also ensures failover if any of the active components (SIP B2BUA) fail. It can also forward a call to the EF Media server for initial (Conversational) AI treatment, and then execute an explicit transfer/ forward to a third party voice component.
CX SIP Proxy can act as a replacement of CUSP. For more information see CX SIP Proxy as a CUSP replacement
Technical Overview
The following diagram illustrates how SIP Proxy handles the call flow. The description is given below the diagram.
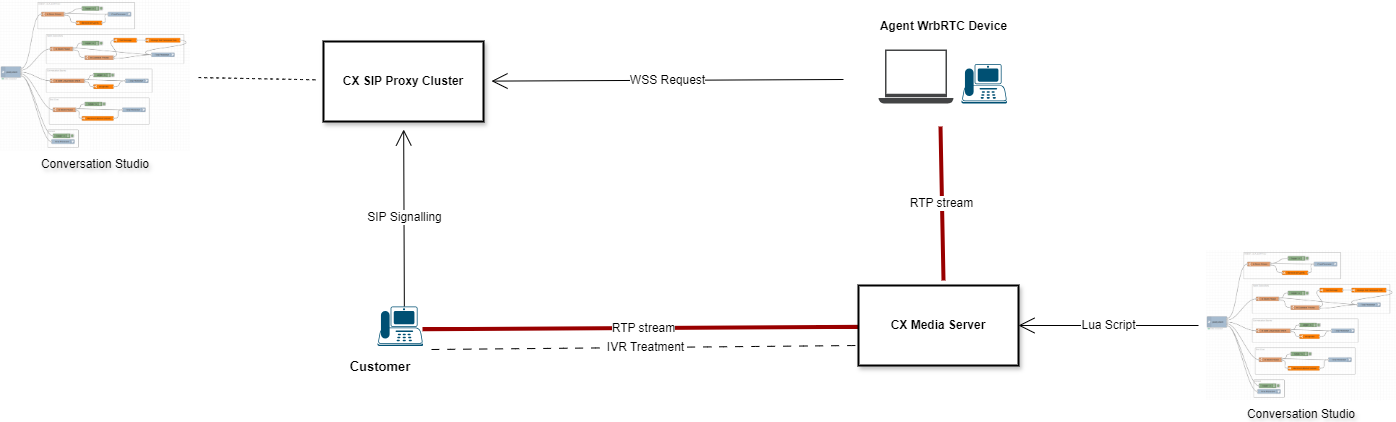
Call Flow
-
Call Initiation:
-
A customer initiates a call that is first received by the CX SIP Proxy. This component is responsible for handling all initial SIP signaling activities associated with incoming calls.
-
-
Configuration Verification:
-
Upon receiving the call, CX SIP Proxy consults its configuration files, which contain routing details generated by Conversation Studio. These configurations direct how calls to certain Directory Numbers (DNs) should be handled.
-
-
Call Routing:
-
Based on the DN specified in the incoming call, CX SIP Proxy identifies the appropriate routing path. It then forwards the SIP signaling to the corresponding DN within the CX Media Server.
-
-
IVR Script:
-
Once the CX Media Server receives the SIP signaling, it initiates the IVR script and establishes an RTP stream with the caller. This connection is responsible for the actual audio exchange between the customer and the system. This script, which is defined and stored within the Media Server as per the configurations set in Conversation Studio, guides the interaction with the customer.
-
-
Transfer to Agent:
-
Each agent is connected to the system via a WebRTC connection that is registered through a WebSocket Secure (WSS) connection to the CX SIP Proxy. If the customer expresses the intent to speak directly with an agent by selecting the corresponding option, the CX Media Server, executes the transfer of the call to the agent extension. The RTP stream flows from the customer through the Media Server to the agent’s extension registered to the CX SIP Proxy.
-
Features and Capabilities
Following are the features of CX SIP Proxy:
|
Features |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Proxy for SIP Unified Communications signaling |
Provides proxy functionality for SIP-based communication, allowing for the routing of signaling messages between different endpoints in a network. This functionality is being provided through the use of the core tm (Transaction Management) module and the dispatcher module for load balancing and routing of SIP messages to endpoints.
|
|
Signaling Support |
Supports a wide range of signaling protocols for voice. |
|
Address Resolution |
Provides support for address resolution using DNS for translating phone numbers into SIP addresses.
|
|
TCP, User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and Transport Layer Security (TLS) |
Supports both TCP and UDP for SIP message transport, as well as TLS for secure transport. This is provided through the use of the proto module for protocol handling and tls module for TLS support.
|
|
Redundancy and high availability options |
Provides support for redundancy and high availability through the use of load balancing and failover mechanisms. |
|
SIP header manipulation |
Provides powerful SIP header manipulation capabilities, allowing for the modification, addition, and removal of SIP headers. This is achieved through the use of the hdr module that provides various functions for accessing, modifying, and manipulating SIP headers.
|
|
Support for IPv4 and IPv6
|
Supports both IPv4 and IPv6 network protocols for SIP communication, allowing for seamless communication between different network types. This is achieved through the use of the proto module that supports both IPv4 and IPv6 transport protocols.
|
|
Call Admission Control |
Provides support for call admission control. This allows for the control of call traffic and resource allocation. This is achieved through the use of the CAC (Call Admission Control) module that provides various functions for monitoring and controlling call traffic. |
|
Dynamic Call Routing and Load Balancing |
Provides support for dynamic call routing and load balancing, allowing for the intelligent routing of call traffic based on various parameters such as caller ID, user location, and call quality. This is achieved through the use of the dispatcher module, which provides advanced routing and load balancing capabilities. |
|
QOS Support |
Provides support for quality of service (QoS) through the use of differentiated services code point (DSCP) and IP precedence marking. This allows for the prioritization of SIP traffic and the allocation of network resources based on traffic priority. This is achieved through the use of the textops module, which provides functions for setting and manipulating DSCP and IP precedence values.
|
|
Monitoring and reporting through syslog, SNMP |
Provides support for monitoring and reporting through various methods such as syslog, SNMP, and SNMP traps. This allows for the monitoring of SIP traffic, call quality, and system performance. This is achieved through the use of the syslog module for logging, and the snmpstats module for SNMP support. |