API Authorization makes sure that only users with the right permissions can access specific APIs. In our setup, we are using Application Gateway and IAM for implementing authorization. The authz-keycloak plugin in Application Gateway handles authorization by validating user tokens and permissions before requests reach backend services.
Architecture Diagram
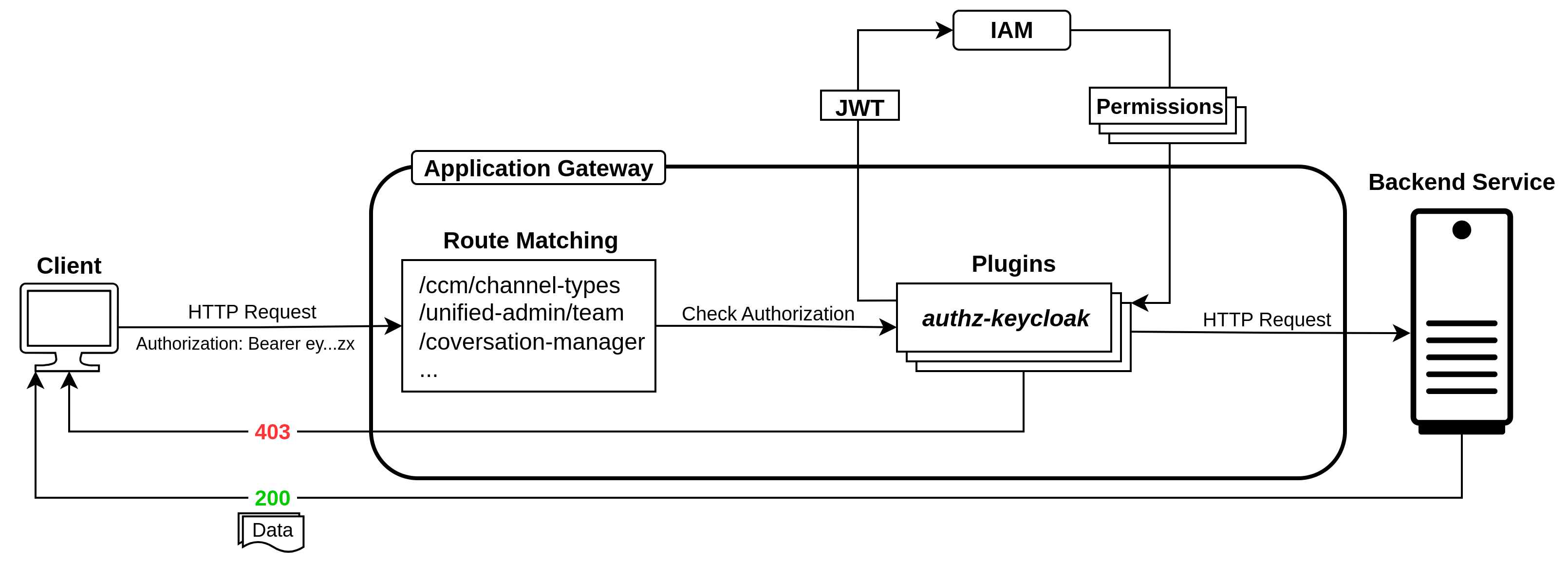
How It Works
The flow of authorization can be understood as follows:
-
Client Request
-
A client sends a request to an API exposed through Application Gateway.
-
The request contains a JWT (JSON Web Token) issued by IAM after successful authentication.
-
-
Route Matching
-
Application Gateway checks the incoming request and matches it with the configured route (e.g.,
/ccm/channel-types,/unified-admin/team,/conversation-manager). -
While matching, Application Gateway also checks whether authorization is enabled for that route.
-
If authorization is enabled, the
authz-keycloakplugin is triggered. -
If authorization is not enabled, the request is simply forwarded to the backend service without additional checks.
-
-
-
Authorization with IAM
-
When enabled, the
authz-keycloakplugin in Application Gateway reads the JWT from the request. -
It communicates with IAM to check if the token is valid and if the user has the required permissions for the requested route.
-
-
Decision
-
If the JWT is valid and the user has permission, the request is forwarded to the backend service. The backend responds with data (HTTP 200).
-
If the token is invalid or the user lacks permission, Application Gateway immediately blocks the request and returns HTTP 403 Forbidden without reaching the backend.
-
Why Use authz-keycloak
-
Centralized Authorization: Permissions are managed in IAM, not spread across multiple services.
-
Early Blocking: Unauthorized requests are stopped at the gateway, saving backend resources.
-
Seamless Integration: Application Gateway and IAM work together through JWTs and the plugin.
To configure/customize API Authorization, see API Authorization Guide.