Queues are the backbone of your contact center's routing system. Think of them as smart waiting areas that ensure your customers reach the right agent at the right time.
Here's how it works:
-
Customer contacts you through any channel (voice, chat, email, etc.)
-
The request is automatically placed in the appropriate queue
-
Our system finds the best available agent based on skills and criteria
-
Customer gets connected to the most qualified agent
This ensures faster resolution times and better customer satisfaction.
Getting Started with Queues
Before creating queues, ensure you have:
-
Administrator access to the system
-
Understanding of your team's skills and structure
-
Knowledge of your channels and service requirements
To access Queue Management:
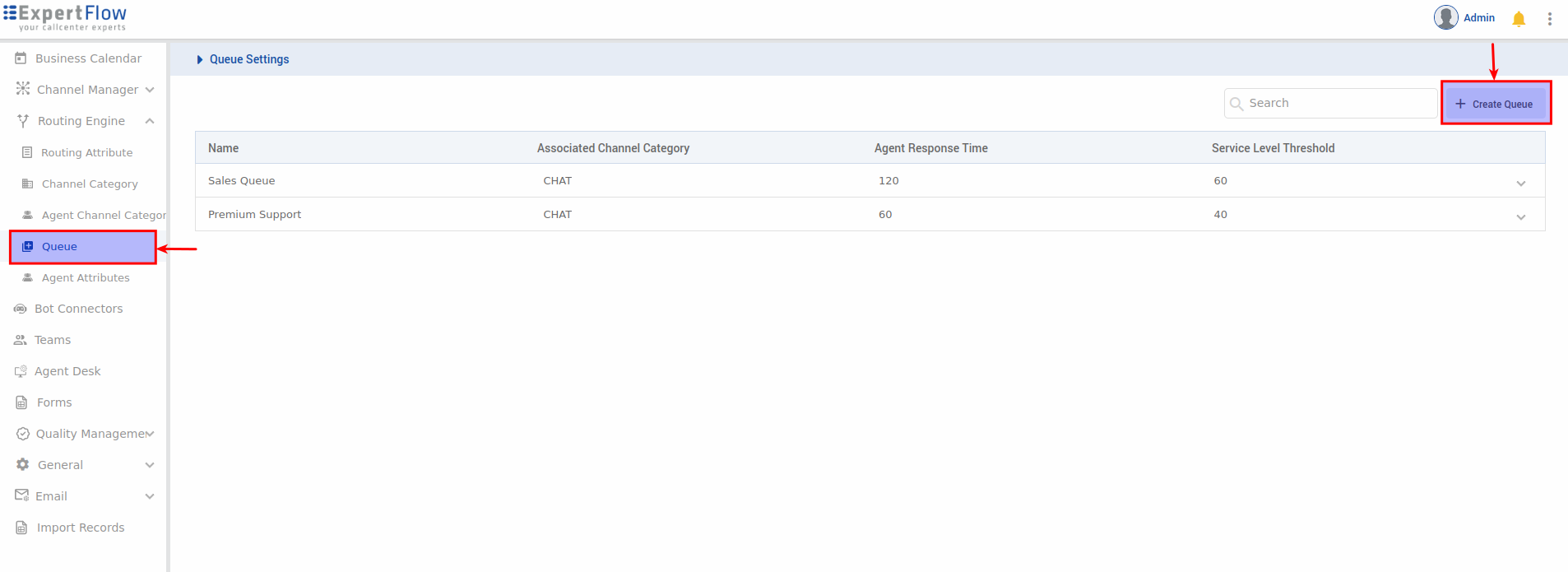
-
In the left panel, under Routing Engine, select Queue
-
You'll see all existing queues and a "Create Queue" button in the top right
Creating Your First Queue
Follow these steps to create a new queue:
-
Click "Create Queue"
-
Fill in the required fields (detailed in next section)
-
Configure your routing steps (see section 5)
-
Save and activate your queue
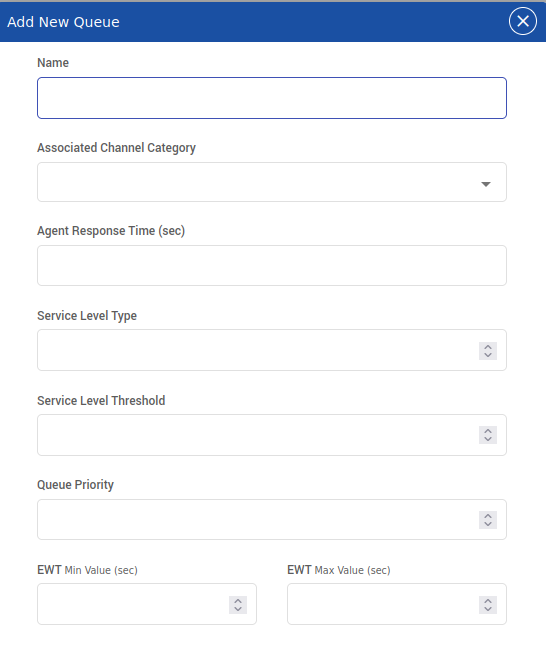
Queue Configuration Fields Explained
Essential Settings
Name
-
Choose a clear, descriptive name (e.g., "Technical Support - Premium", "Sales - English")
-
Use consistent naming conventions across your organization
Associated Channel Category
-
Select the communication channel this queue will handle
-
Each queue can only handle one type of media (voice, chat, email, etc.)
Agent Response Time
-
Sets your Service Level Agreement (SLA) target
-
Measured in seconds - this is how quickly you aim for your agents to respond to customers
Advanced Settings
Service Level Type
-
Defines how you measure service level success for reporting purposes
-
Choose from predefined service level calculation methods:
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
-
See Key Reporting Concepts for detailed explanations
Service Level Threshold
-
The target time (in seconds) for requests to be answered
-
Requests answered within this time are considered "within service level"
-
Used for SLA reporting and performance tracking
-
Set according to your business policies and customer expectations
Queue Priority
-
Determines the priority level when multiple queues compete for agents
-
Higher priority queues are served before lower priority ones
-
Useful for VIP customers or urgent request types
-
See Queue Priority documentation for more details
EWT Min Value & EWT Max Value
-
EWT = Estimated Wait Time shown to customers while they wait
-
Min Value: Minimum wait time displayed (even if actual wait is shorter)
-
Max Value: Maximum wait time displayed (caps the estimate shown to customers)
Important Notes:
-
If you leave EWT values empty, the system shows actual calculated wait times
-
Min Value must be less than Max Value
-
Maximum possible value: 2,147,483,647 seconds
For detailed EWT information, see our Queue Wait Time documentation.
Managing Queue Steps
Steps are routing rules that determine which agents can handle requests in this queue. Think of them as filters that find the perfect agent match.
To access step management:
After creating your queue, click the dropdown arrow (⋮) at the rightmost column to access step management.

Here you can Add/Modify/View Queue Steps.
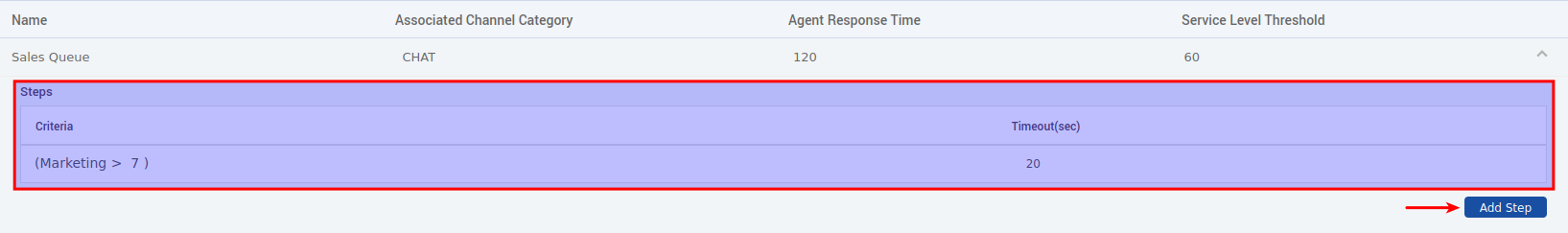
How Steps Work
Step Priority: Steps are executed in order (Step 1 first, then Step 2, etc.)
-
Maximum 10 steps per queue
-
Each step has a timeout period
-
If no agent is available in Step 1, the system moves to Step 2 once the step timeout expires
Step Timeout: How long the system waits at each step before moving to the next
-
Measured in seconds
-
Balances speed vs. finding the perfect agent match
Creating Routing Rules
Terms/Criteria
Steps are created using expressions. Each expression consists of terms that compare an agent's skill to a required value:
-
Example:
Spanish >= 8(agent must have Spanish proficiency of 8 or higher) -
Example:
Location = Boston(agent must be located in Boston)
Expressions
Combine multiple terms using AND/OR logic:
-
(Boston = true) AND (Spanish >= 8) AND (Technical_Support >= 7) -
This finds Boston-based agents with strong Spanish and technical skills
Evaluation Order: Expressions evaluate left to right
(Boston = true) AND (Spanish >= 8) AND (Technical_Support = 5)
→ true AND true AND false
→ true AND false
→ false (agent doesn't qualify)
Understanding Agent Assignment
Agents are automatically assigned to queues based on their Routing Attributes matching your queue's Steps.
Real-World Example
Scenario: You need agents for Spanish technical support in Boston
Queue Setup:
-
Queue Name: "Technical Support - Spanish - Boston"
-
Step 1:
(Location = Boston) AND (Spanish >= 8) AND (Technical_Support >= 7) -
Step 2:
(Spanish >= 6) AND (Technical_Support >= 7)(relaxed location requirement)
Agent Profiles:
-
Agent A: Boston=true, Spanish=9, Technical_Support=8 → ✅ Qualifies for Step 1
-
Agent B: NewYork=true, Spanish=7, Technical_Support=9 → ✅ Qualifies for Step 2 only
-
Agent C: Boston=true, Spanish=4, Technical_Support=8 → ❌ Doesn't qualify
Result: Spanish customers needing technical help will first be routed to Agent A (perfect match), then Agent B if A is unavailable.
Multiple Queue Example
Queue Q1 has 2 Steps:
-
Step 1 agents: [Agent1, Agent2, Agent3]
-
Step 2 agents: [Agent4, Agent5]
When a customer request arrives:
-
System tries Step 1 agents first
-
If all Step 1 agents are busy, tries Step 2 agents
-
Continues until an available agent is found
Glossary
Agent Response Time: Time by which the agent must respond to a customer request
Associated Channel Category: The communication channel type (voice, chat, email, etc.)
EWT: Estimated Wait Time - calculated prediction shown to waiting customers
Expression: Combination of routing criteria using AND/OR logic
Precision Queue: Advanced queue type that uses multiple routing steps for optimal agent matching
Queue Priority: Determines which queues get served first when multiple queues compete for agents
Routing Attributes: Skills, locations, and capabilities assigned to each agent
Service Level: Performance target (e.g., "answer 80% of calls within 20 seconds")
Service Level Threshold: Target time for requests to be answered to meet service level requirements
Service Level Type: Method used to calculate service level performance for reporting
Steps: Sequential routing rules that determine agent selection priority
Step Timeout: Time the system waits at each step before moving to the next step
Terms/Criteria: Individual skill requirements used in routing expressions (e.g., "Spanish >= 8")
Need help with queue setup? Contact your system administrator or support team.