|
Node |
Decision Node |
|---|---|
|
Description |
Decision node is used to implement conditional branching in an IVR flow, allowing dynamic control based on session data. It evaluates one or more logical conditions using values from CDO, SDO, or ENV sources and determines the next path in the call flow based on whether the combined result is true or false. This node generates conditional logic ( |
Configuration
Each Decision node allows configuration of a single logical block (one if statement), which may contain one or more individual conditions combined using logical operators.
Condition Structure
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Type |
Specifies the logical operation. Only the first condition must use |
|
Source Key |
The left-hand value to compare. This may come from:
|
|
Operator |
The comparison operator to use:
|
|
Target Value |
The right-hand value. Can be one of the following types:
|
Multiple Conditions
-
You can chain multiple conditions using logical operators:
ANDorOR. -
Chaining is left-to-right, meaning execution follows a strict sequential order.
-
Parentheses for grouping are not currently supported — ensure proper logical grouping by design.
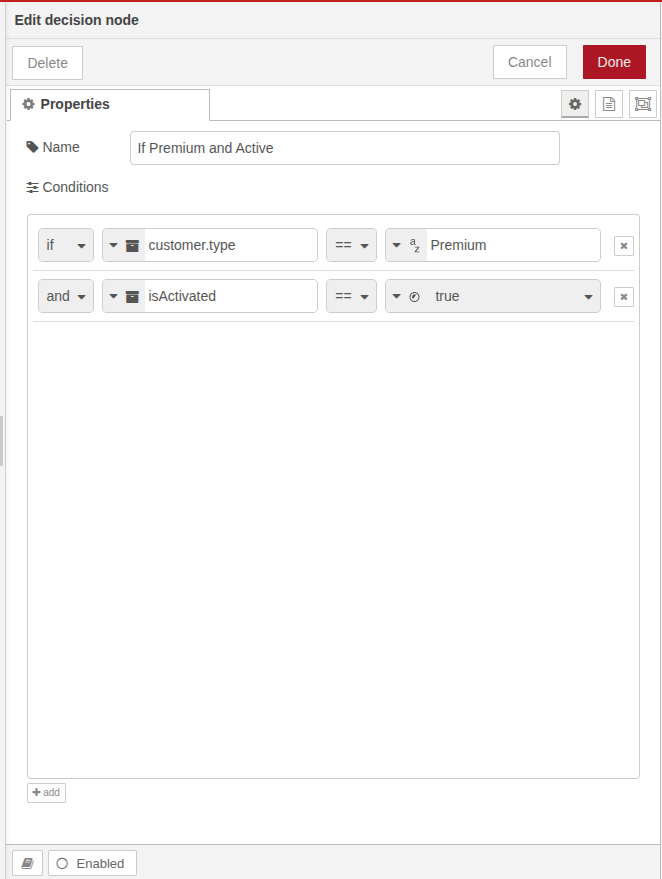
Example
Here we’ve two conditions if customer type is Premium and customer is activated,
Outputs
The Decision node provides two output branches:
|
Output |
Trigger Condition |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Output 1 (True) |
If the overall condition evaluates to |
The flow continues along this path |
|
Output 2 (False) |
If the condition evaluates to |
The alternate flow path is followed |
Best Practices
-
Use one Decision node per logical decision block. If your flow requires branching logic at multiple stages, use multiple nodes in sequence.
-
Use meaningful key references to maintain flow readability.
-
Avoid deeply nested or overly complex logic in one node. Break into simpler decisions where possible.
Example Use Case
Scenario: Route calls based on user language and region.
Conditions:
-
CDO.languageis"fr" -
AND
SDO.regionis not"NA"
Result:
-
If both conditions are met → route to French support
-
Else → route to default support