|
Node |
Exception Node |
|---|---|
|
Description |
The Exception Node is a special-purpose node used to define a fallback flow in case of unhandled or unexpected errors during the IVR execution. It ensures that even if the main flow encounters a failure (e.g., API error, misconfiguration, timeout), the caller experience remains smooth and guided. |
Purpose
-
To gracefully handle unexpected errors in the IVR
-
To ensure that the caller is not left in a dead-end or loop
-
To improve user experience and system reliability
Behavior
-
Exception Node is separated from the main call flow
-
It is directly connected to the Start Node
-
If any runtime error or failure occurs during the IVR, the system jumps to this node’s flow
-
You can design any number of actions after this node — e.g. play a prompt, log the issue, call an API, transfer the call, etc.
Use Cases
-
Play a message like: “We’re experiencing issues. Please try again later.”
-
Log the failure using an API or store the session data
-
Redirect the user to an agent or exit gracefully
-
Track IVR stability metrics by logging exceptions
Usage Notes
-
Only one Exception Node should be used per IVR design
-
It must be connected directly to the Start Node
-
It should not be part of the regular call flow path
Flow Example
├── Main IVR Flow ➝ Nodes ➝ Deploy
└── Exception Node ➝ Prompt ➝ API Call ➝ Hangup
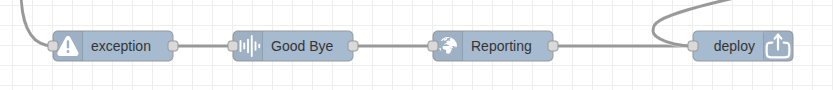
Best Practices
-
Always include an Exception Node in IVR, by design Exception node is mandatory.
-
Keep the fallback prompt clear and courteous
-
Log error details to help with diagnostics and monitoring
-
Avoid looping users back to main flow from the exception branch