Control flow in Conversation Studio is made up of different categories of nodes listed below. These nodes allow users to manage and define how a conversation progresses from start to end. Using control flow nodes, users can design custom flows for various system events, defining the conversation’s path by simply connecting combinations of available nodes.
Please Consider the Following When Creating Custom Flows
The node-red-resilient-hooks plugin described in the “Custom Plugins” section relies on specific lifecycle events from nodes(onReceive / onComplete) to correctly cache and clear messages during processing. Conversation Studio’s built-in nodes, Switch type nodes, and Function type nodes are validated and work correctly with these hooks, other type of Node-RED node types may not trigger these events as expected.
Because of this, using other type of nodes can result in:
-
Messages being cached but never cleared
-
Gradual memory buildup and potential OOM (Out-Of-Memory) crashes
-
Excessive Redis storage consumption
Recommendation
To ensure safe and reliable message processing:
-
✔️ Use only Conversation Studio–provided nodes, Switch nodes, and Function nodes in your flows
-
❌ Avoid using any other type of Node-RED nodes, unless explicitly validated for compatibility with the resilient-hooks mechanism
Key Terminologies
Before diving into details, here are the essential terms used in Conversation Studio.
|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Flow |
A visual representation of conversation logic connecting various nodes |
|
Intent |
Events processed by Conversation Manager (e.g., CONVERSATION_STARTED, AGENT_SUBSCRIBED) |
|
Slot |
Memory storage in the cache that holds current event details for a conversation |
|
Entity |
Data objects containing conversation context and event information |
|
Node |
A Node is a building block that perform specific functions within a flow |
How conversation studio Controls Conversation
The conversation studio controls the conversation flow from creation to closure. It monitors and controls the communication exchange between the customer and the business resources (Bot, Agent) and takes decisions upon intents passed by the Conversation Manager. The intents are basically the events that are processed by Conversation Manager. The events on which we want to perform custom actions are then passed to Conversation Studio. The list of all events are mentioned here.
The studio gives control to the business to customize the behavior of conversation handling. For example, send a greeting message as customer joins a conversation or send a survey message to the customer when agent leaves.
The Conversation Studio decides to close a channel session at any point in time, based on the bot training data. For instance, it may close a session if one of the following happens:
-
The customer leaves the chat
-
The agent leaves the chat and no one else is in the conversation
-
Customer response timeout expire
The sequence of events in given as follows:
-
Conversation Manager delivers the event to Conversation Studio by calling the exposed endpoint
/intentwith the payload in below format-
Conversation Studio exposes a webhook at
/intentwith the POST method, that can be used by Conversation Manager to deliver the actions occurring within the system, for example,CONVERSATION_STARTED,AGENT_SUBSCRIBEDetc.
-
{
roomId: RoomId, // Type: string
conversation: ConversationObject, // Type: Object
intent: EventName, // Type: string
entities: EntitiesObject, // Type: Object
metadata: MetadataObject // Type: Object
}
-
Conversation Studio does the internal processing and passes the control to the relevant INIT node with the payload in below format:
-
It merges the slot in redis for this given roomId and update the slots object in this msg object as well. Slots are just the place in memory(Redis) to hold the current event details.
-
msg = {
_msgid: "...",
req: { ... }, // Request object
res: { ... }, // Response wrapper
payload: {
roomId: "12345",
conversation: {},
intent: "CHANNEL_SESSION_STARTED",
entities: {}, // Object of Map Type that includes the complete CimEvent object as value agains the key "cimEvent".
metadata: {},
messages: [],
slots: { ... }
}
}
-
Init Node then triggers the complete flow.
-
If any action needs to be executed, it is delivered to the Conversation Manager on the webhook
/controller-webhook
{
"conversationId": "<conversation_id>",
"channelSession": "<last_used_channel_session>",
"messages": [
{
"mode": "",
"body": {
"type": "ACTION",
"name": "<ACTION_NAME>",
"data": {
/* action-specific data */
}
}
}
]
}
Databases
Conversation Studio uses the following database for its working.
-
Redis: Conversation Studio stores the slots linked to a room, messages cache and context storage in the Redis.
Custom Plugins
The Conversation Studio uses following plugins for its functionality
-
node-red-auth-keycloak: The custom plugin to authenticate and authorize users from Keycloak.
-
node-red-context-redis: This is a custom context storage that is used by default in the Conversation Studio instead of memory or localfilesystem.
-
node-red-resilient-hooks: This hook ensures that messages currently being processed by the Conversation Studio are not lost between flow changes by the user
Please refer to this document for details on the default flows that come with the deployment Conversation Studio.: Default Flows
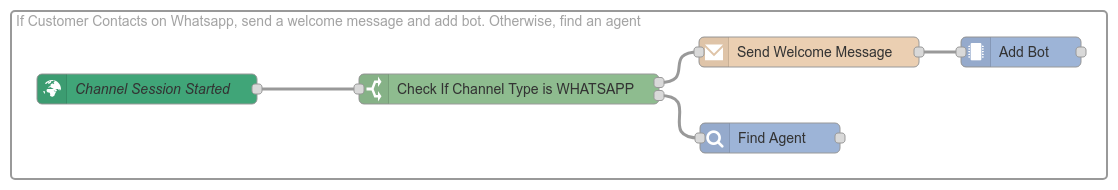
Following are some example system behaviors, that can be easily defined using the Control Flow nodes.
-
Adding a bot when a conversation starts
-
Removing an agent when their SLA expires
-
Sending a text message when a conversation is pause
Nodes
The list of nodes for control flow are given as follows:
|
Node |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The Condition Node serves as a checkpoint in our workflow. It comprises a bunch of nodes that check specific conditions against the input payload and route the message to one of two paths. Most condition nodes accept one input and have two outputs for true/false conditions. |
|
|
Actions nodes |
|
|
The Survey Message |
|
|
The Conversation Controller Reminder nodes can be used to schedule and unschedule reminders and define flows to be executed when a certain reminder triggers. |
|
|
The Text Message |
|
|
The Init Node |
.png?cb=c084ef5f5b3d1a249987ca4a0840fad7)

.png?cb=c92adda91909e1d2b47c7a02fde123ed)